7.5.2 创建JSON
正如上一个小节所示,分析JSON的方法和分析XML的方法是非常相似的。同样地,如图7-9所示,创建JSON的方法和创建XML的方法也是相似的。
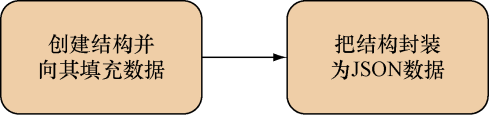
代码清单7-12展示了把Go结构封装为JSON数据的具体代码。
代码清单7-12 将结构封装为JSON
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
)
type Post struct { ❶
Id int `json:"id"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Author Author `json:"author"`
Comments []Comment `json:"comments"`
}
type Author struct {
Id int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
}
type Comment struct {
Id int `json:"id"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Author string `json:"author"`
}
func main() {
post := Post{
Id: 1,
Content: "Hello World!",
Author: Author{
Id: 2,
Name: "Sau Sheong",
},
Comments: []Comment{
Comment{
Id: 3,
Content: "Have a great day!",
Author: "Adam",
},
Comment{
Id: 4,
Content: "How are you today?",
Author: "Betty",
},
},
}
output, err := json.MarshalIndent(&post, "", "\t\t") ❷
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error marshalling to JSON:", err)
return
}
err = ioutil.WriteFile("post.json", output, 0644)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error writing JSON to file:", err)
return
}
}
❶ 创建结构并向里面填充数据
❷ 把结构封装为由字节切片组成的JSON 数据
跟处理XML时的情况一样,这个封装程序使用的结构和之前分析JSON时使用的结构是相同的。程序首先会创建一些结构,然后通过调用 MarshalIndent 函数将结构封装为由字节切片组成的JSON数据( json 库的 MarshalIndent 函数和 xml 库的 MarshalIndent 函数的作用是类似的)。最后,程序会将封装所得的JSON数据存储到指定的文件中。
正如我们可以通过编码器手动创建XML一样,我们也可以通过编码器手动将Go结构编码为JSON数据,图7-10展示了这个过程。
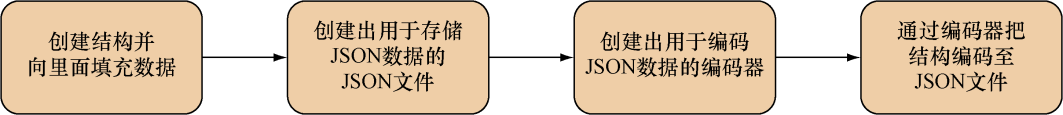
代码清单7-13展示了 json.go文件 中包含的代码,这些代码可以根据给定的Go结构创建相应的JSON文件。
代码清单7-13 使用 Encoder 把结构编码为JSON
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io"
"os"
)
type Post struct { ❶
Id int `json:"id"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Author Author `json:"author"`
Comments []Comment `json:"comments"`
}
type Author struct {
Id int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
}
type Comment struct {
Id int `json:"id"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Author string `json:"author"`
}
func main() {
post := Post{
Id: 1,
Content: "Hello World!",
Author: Author{
Id: 2,
Name: "Sau Sheong",
},
Comments: []Comment{
Comment{
Id: 3,
Content: "Have a great day!",
Author: "Adam",
},
Comment{
Id: 4,
Content: "How are you today?",
Author: "Betty",
},
},
},
jsonFile, err := os.Create("post.json") ❷
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating JSON file:", err)
return
}
encoder := json.NewEncoder(jsonFile) ❸
err = encoder.Encode(&post)
if err != nil { ❹
fmt.Println("Error encoding JSON to file:", err)
return
}
}
❶ 创建结构并向里面填充数据
❷ 创建用于存储数据的JSON 文件
❸ 根据给定的JSON文件创建出相应的编码器
❹ 把结构编码到JSON文件里面
跟之前一样,程序会创建一个用于存储JSON数据的JSON文件,并通过把这个文件传递给 NewEncoder 函数来创建一个编码器。接着,程序会调用编码器的 Encode 方法,并向其传递一个指向 Post 结构的引用。在此之后, Encode 方法会从结构里面提取数据并将其编码为JSON数据,然后把这些JSON数据写入创建编码器时给定的JSON文件里面。
关于分析和创建XML和JSON的介绍到这里就结束了。虽然最近这两节介绍的内容可能会因为模式相似而显得有些乏味,但这些基础知识对于接下来的一节学习如何创建Go Web服务是不可或缺的,因此花时间学习和掌握这些知识是非常值得的。